133 BC
| Millennium: | 1st millennium BC |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | 3rd century BC · 2nd century BC · 1st century BC |
| Decades: | 160s BC · 150s BC · 140s BC · 130s BC · 120s BC · 110s BC · 100s BC |
| Years: | 136 BC · 135 BC · 134 BC · 133 BC · 132 BC · 131 BC · 130 BC |
| 133 BC by topic |
| Politics |
|---|
| Categories |
|
| Gregorian calendar | 133 BC CXXXII BC |
| Ab urbe condita | 621 |
| Ancient Egypt era | XXXIII dynasty, 191 |
| - Pharaoh | Ptolemy VIII Physcon, 13 |
| Ancient Greek era | 161st Olympiad, year 4 |
| Assyrian calendar | 4618 |
| Bengali calendar | −725 |
| Berber calendar | 818 |
| Buddhist calendar | 412 |
| Burmese calendar | −770 |
| Byzantine calendar | 5376–5377 |
| Chinese calendar | 丁未年 (Fire Goat) 2564 or 2504 — to — 戊申年 (Earth Monkey) 2565 or 2505 |
| Coptic calendar | −416 – −415 |
| Discordian calendar | 1034 |
| Ethiopian calendar | −140 – −139 |
| Hebrew calendar | 3628–3629 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | −76 – −75 |
| - Shaka Samvat | N/A |
| - Kali Yuga | 2968–2969 |
| Holocene calendar | 9868 |
| Iranian calendar | 754 BP – 753 BP |
| Islamic calendar | 777 BH – 776 BH |
| Javanese calendar | N/A |
| Julian calendar | N/A |
| Korean calendar | 2201 |
| Minguo calendar | 2044 before ROC 民前2044年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | −1600 |
| Seleucid era | 179/180 AG |
| Thai solar calendar | 410–411 |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 133 BC. |
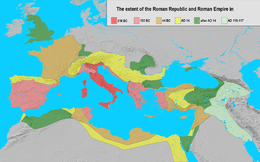
The Roman empire in 133 BC (in dark and light red)
Year 133 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scaevola and Frugi (or, less frequently, year 621 Ab urbe condita). The denomination 133 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Events
By place
Roman Republic
- Lucius Calpurnius Piso Frugi, as consul, is sent against the slaves in Italy. Gaius Marius serves under Publius Cornelius Scipio Aemilianus at Numantia.
- Scipio Aemilianus captures Numantia,[1] after a siege of eight months, suffering famine and pestilence. The remnant population of 4,000 citizens, surrender and set their city on fire. Thus ends the Numantine War.
- Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus, is elected tribune of the people. He attempts to pass a law to redistribute the public land to benefit small landowners. Opposed by wealthier factions in the Roman Senate, he is killed by a group of Senators and their followers that same year.
- The Kingdom of Pergamum is deeded to Rome.
China
- June – A large army of the Han Dynasty, under commanders such as Li Guang, attempt to ambush the Xiongnu leader in the Battle of Mayi. The plot fails, and the battle is determined a draw.
Births
Deaths
- Attalus III, king of Pergamon. In his will, he makes the people of Rome his heirs (b. 170 BC)
- Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus the Roman tribune (assassination) (b. 168 BC)
References
- ↑ Davis, Paul (2001). Besieged: An Encyclopedia of Great Sieges from Ancient Times to the Present. ABC-CLIO. p. 29.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/20/2013. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.